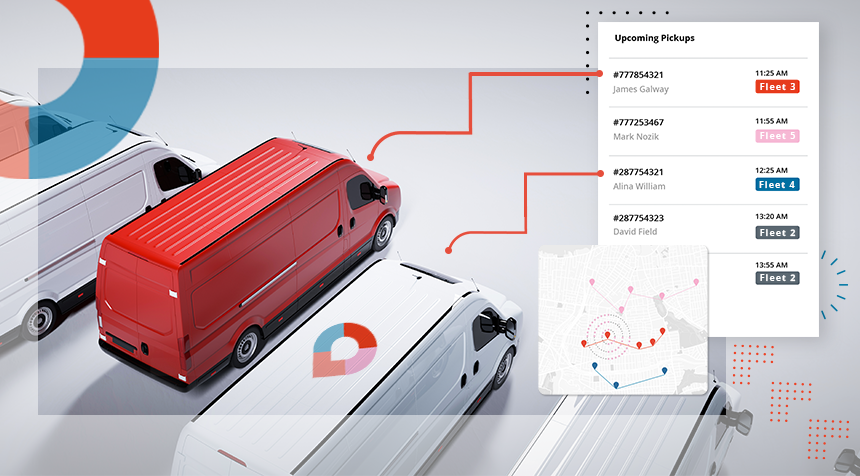
Despite the growing demand for same-day delivery, there are always situations where people prefer to spend less money and receive their goods or services later. But with today’s customer expectations, scheduled delivery does not have to be slow, and should definitely be convenient.
With consignees demanding more flexibility from their delivery options, retailers, shippers and delivery providers need to understand how to optimize this delivery model – and when to offer their customers other delivery options as well.
This article covers everything you need to know about:
- How a scheduled delivery service differs from other major shipping options
- Challenges facing scheduled delivery services today
- Best practices for scheduled delivery options, including when to use other alternatives
- How technology can help you deliver efficiently and cost-effectively for better customer experiences
First, the basics:
What is scheduled delivery?
Scheduled delivery is a method of shipping that plans the date of delivery based on a fixed time window that is convenient for the shipper, the carrier or the consignee. The delivery date may be set by the shipper or carrier or selected by the consignee from a range of one or more delivery options.
How scheduled delivery works
In some cases, the shipper may instruct the carrier to deliver on a specific date, or to choose the first available delivery date among a range of available dates. Other times, the carrier may set the delivery time based on their internal policies and route optimization planning. Alternatively, the delivery time and date can be set by the customer at checkout, if the shipper or carrier allows this option.
The customer receives a delivery estimate, which shows when they can expect to receive the order.
Estimated delivery date vs. actual delivery date
The date when the customer is scheduled to receive the delivery is defined in tracking information as the “estimated delivery date.” The day the customer actually receives it is the actual “delivery date.”
The estimated date of delivery can be changed due to a delivery exception, such as a weather emergency. In this case, the shipment will be classified as “delivery pending,” and the customer may receive a rescheduled delivery pending message informing them of the next available delivery time slot. This allows for flexible scheduling adjustments in the case of an unexpected event.
Why scheduled delivery is still popular
Scheduled or ‘planned’ delivery is a popular shipping option because it usually allows for delivery at a time window which fits the needs of all parties involved, including the shipper, the carrier and the customer. It usually costs significantly less than on demand or same-day delivery as well.
It’s a great option for carriers and shippers, who have enough advanced notice to optimize routes as well as optimally filling delivery vehicles to full capacity and potentially reducing the runs per delivery vehicle.
A potential disadvantage is that the customer may be locked into a delivery time that is slower than what they would prefer. On the other end of the process, the shipper or carrier also may be locked into a service level agreement (SLA) which is less than ideal. If they are forced to make sudden changes to the delivery SLA, the customer may perceive this as a failure to follow through, particularly if they have paid extra for a specific delivery day or window.
Scheduled vs. on demand delivery
Scheduled delivery stands in contrast to on demand delivery, another increasingly popular delivery option. Whereas scheduled delivery involves a planned delivery time window which may be fixed by any party involved in the shipping process and usually represents a compromise between the needs of all parties involved, with on demand delivery, the delivery takes place a short time after the order has been made (within hours or even minutes).
On demand delivery is common for local delivery, with orders fulfilled from stores, micro-fulfillment centers (MFC’s) or urban warehouses; scheduled deliveries are still most often fulfilled from warehouses belonging to retailers, other shippers, or 3pl logistics providers.
As with planned delivery, on demand delivery management may be handled in-house or by a third party delivery provider. When using an outside delivery service, the delivery timeline and other variables are subject to the policies of the carrier. For example, the final delivery destination may be changed with on demand delivery just as it may with planned delivery options.
The best option? Offer both.
On demand and planned delivery serve two different purposes: One is fast, but usually more expensive, while the other is usually free but slower. The best companies provide both options, giving customers additional choice over their order fulfillment. For example, a customer may want an item the same day, even if this comes with a higher delivery fee and inconvenience for the shipper.
Scheduled delivery vs. subscription delivery
Subscription delivery represents an alternative to both scheduled and on demand delivery. With subscription delivery, delivery dates are fixed on a regular schedule, such as every 30 days.
The delivery schedule may be initially set by the customer, the shipper or the carrier. Typically, the customer selects a date for delivery day or timeframe (e.g. 2 day delivery, 4-5 day delivery, etc.). Once the original delivery date is set, it usually doesn’t change. However, delivery exception events may cause delivery commitment changes, including to the estimated delivery date. The customer also may request a different delivery date, but unlike with scheduled delivery, such a request implies a change to the date of delivery on a recurring basis going forward.
One of the advantages of subscription delivery is that it allows customers to pre-order future shipments on a recurring basis instead of placing an order for the same item periodically. This is convenient for the customer, and it encourages repeat business.
However, subscription delivery offers less flexibility than either scheduled or on demand delivery. That means fewer opportunities to provide customers with convenient delivery options, compared with scheduled or on demand delivery.
When to use on demand or subscription delivery instead of scheduled delivery?
Each method of shipping has its pros and cons and best uses:
- Scheduled or planned delivery is useful when you want to offer customers efficient, affordable delivery and they don’t necessarily require next-day or same-day delivery.
- On demand is useful if your customers demand fast delivery and both you and they can afford the extra costs.
- Subscription delivery is useful if your customers need specific items on a regular periodic schedule.
These methods aren’t necessarily mutually exclusive. You may offer different options for different products, customers or scenarios. For example, customers who pay an extra fee may get on demand shipping at a reduced rate.
Challenges of scheduled delivery
Planned delivery operations face a number of significant challenges, ranging from customer expectations to internal challenges meeting scheduled delivery timetables. Let’s look at some of the most common problems facing planned delivery operations before considering best practices designed to address these issues and optimize your delivery options.
Customer Expectations
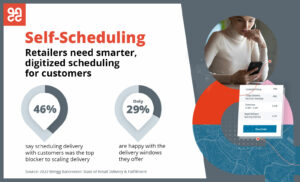
The issue is simple: customers will go wherever there are more, and better, delivery options – as will shippers. In a recent survey, almost 1 in 2 retailers voiced some level of dissatisfaction with the delivery and pickup options they offered customers; 39% found digitized scheduling too expensive or complicated to offer. Yet in a logistics report, 61% of respondents said their shippers were requesting automated scheduling.
Self-scheduling is just one element of the delivery experience which retailers and logistics providers struggle to provide end customers.
Short delivery windows
Major shipping companies now offer two-day delivery, next-day delivery and even same-day delivery. Often their scheduled service will include delivery in a tight two or four-hour window for free as the default option, or at least as an added service plan.
These companies set the standard for what customers want from their delivery. However, many delivery services still offer only multi-day delivery windows. If delivery windows are too long, customers will be dissatisfied and look elsewhere for their products or logistics services.
Manual delivery scheduling is costly
Outdated or disparate technologies can make it hard for delivery and logistics service providers to deliver efficiently and at scale while making their SLAs.
Staging and dispatching scheduled deliveries is traditionally a low-tech process. For many logistics providers, staging is as simple as moving packages from a pile on a warehouse floor to a truck after it arrives. Too often, this is still a pen and paper process.
Scheduling – Many companies still schedule delivery via phone, after the order has been made online. This wastes manpower resources, creating potential problems when there aren’t enough staff members available to manage phone calls.
The time spent keeping customers and carriers on hold causes delays which can contribute to shipments missing their delivery SLAs. This manual process can drive customers away and reduce the number of customers who can be serviced, cutting into profits on two fronts.
Moreover, using the phone to schedule deliveries tends to go hand-in-hand with manual, reactive customer service. Instead of providing customers with digitized smart scheduling and automated delivery updates, too many shippers and carriers still provide customers with delivery estimate information by phone, or manually send them a delivery status update, leading to high WIZMO (“Where is my order”) rates that cost manpower hours and put a damper on the delivery experience.
Meeting scheduled delivery date targets requires precise planning
Using inefficient technology can have a ripple effect by undermining delivery route planning.
To consistently deliver on time, the shortest routes need to be identified, multiple delivery stops need to be consolidated, customer schedules need to be considered and timetables need to be drawn up. Inefficiencies or mistakes in any of these areas can cause shipments to miss their scheduled delivery date.
Last-minute changes and delivery exception events can disrupt your plans
Even the best planning can be disrupted by unplanned events. For example, a customer may request a change to their final delivery destination. Or delivery exception events such as snowstorms, flooding, flat tires or orders for out-of-stock items may interfere with the scheduled delivery date.
If you’re not prepared to deal with these kinds of events, and don’t have the tools to manage them in real time, then meeting delivery obligations can be challenging.
Adjusting to changes requires real-time communication with carriers and customers
Making effective adjustments to delivery exception events requires the ability to communicate with carriers and customers in real time. For example, using automated delivery notifications allows shippers to keep in touch with carriers and customers.
If a customer requests a change to the delivery address, this can be communicated to carriers through real-time notifications. When there are no automated delivery system notifications in place, it’s a recipe for miscommunication and failed delivery attempts, resulting in 4-5x the cost for rescheduled deliveries when considering added mileage, fuel, and driver pay
Creating efficient, flexible and cost-effective scheduled delivery
To achieve efficiency at scale around planned deliveries, the delivery strategy must include accurate planning, the use of advanced technologies, and fully connected resources and processes with a focus on how they affect the customer.
Let’s look more closely at some of the best practices:
1. Connect your systems
If companies want to offer real-time capabilities, they need to be integrated with systems belonging to the relevant vendors, 3pl logistics providers, or shippers.
Each company’s backend data must be synced seamlessly to a centralized repository. Changes in any system – like order cancellations or changes in the delivery window selected – are then automatically updated in both the central and end systems.
2. Estimate travel time accurately
One of the most important keys to meeting the planned delivery date and time is accurate travel time estimations. Meeting delivery SLAs requires careful, accurate delivery time estimates. This depends on prudent consideration of routes, selection of the shortest routes and accurate estimation of distances.
It also depends on being able to factor in speed limits, traffic, construction and other variables which can impact travel time and affect the delivery SLA. If you have to make an adjustment, such as when a customer changes their final delivery destination, you’re able to estimate your new timetable accurately.
3. Factor in time for drop-offs

Accurate delivery estimates don’t just depend on travel time calculations. They also require factoring in time to drop off items at the scheduled stops.
Some stops may only require a minute to open a mailbox; others may require more time to get a signature or drop off bulk deliveries. In some cases, special delivery equipment may need to be available -for example, threshold or room of choice.
For delivery stops which involve picking up items from customers, such as picking up recyclable containers, reverse logistics needs to be factored into your delivery calculations.
4. Schedule deliveries based on priority
Another important tactic is to schedule your delivery timetable based on which shipments need to arrive first.
For example, if a customer has ordered overnight delivery, you may need to combine their shipment with another route run in order to meet your delivery commitment. Or if a customer has updated their final delivery destination, this may require adjusting priorities to meet your new scheduled delivery time.
Intelligent dispatch
When you or your regular carriers don’t have the capacity do meet demand, and need to engage additional fleets, you can use smart dispatch software that automatically assign spillover orders to a specific driver, team or fleet.
5. Consolidate trips
Meeting the promised delivery time typically requires consolidating trips. The more deliveries you can make per trip, the less mileage you have to travel, making it easier for you to provide the delivery options your customers want. In the process, you can cut your average cost to deliver. We see this with LTL freight carriers who consolidate their freight with other shippers to reduce the shipping cost.
6. Use software to optimize route planning
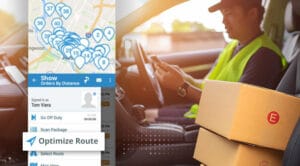
Providing scheduled delivery shipping options and delivering on time requires the use of intelligent dispatch and routing software.
Today’s cutting-edge delivery software can relieve you of the need to optimize routes manually by factoring in all the relevant data you need for timely deliveries and using it to automatically calculate your delivery schedule. This includes data about your fleet, carriers, customers, inventory and orders.
To harness this data for on-time last-mile delivery, all relevant information is processed through a central system which generates optimized route maps and schedules and keeps them updated.
As orders travel along shipping routes, the system keeps track of where inventory is at all times. This gives shippers, carriers and customers the ability to communicate through real-time updates.
If there is a change to the delivery address, then a new optimized route can be calculated automatically and relayed to the driver, while an automated notification is sent to the customer.
7. Communicate with Customers
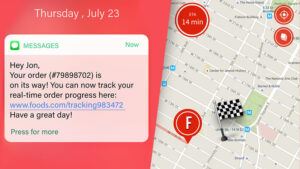
Everyone wants to stay updated on tracking information. This can be done through a scheduled ‘delivery pending’ message notification system which uses texts or emails to send customers the tracking number and update them on the order status and location. This lets customers see in real time when there are changes to their delivery time.
Keeping delivery information up-to-date depends on real-time communication between shippers, carriers and customers.
Customers can be kept in the loop both through access to a central portal with tracking information and through scheduled delivery pending message notifications delivered via text or email.
This type of communication system lets customers know where their package is at all times. It alerts them if they should expect a change because of an exception event. It further allows them to request last-minute changes, such as asking for a final delivery destination reroute to different delivery zip code.
Add-on services
Having integrated data and delivery operations, with full visibility, opens up opportunities for add-on services and loyalty programs that can defray the cost of deliveries.
For example, some premium service includes delivery within 2 or 4-hour windows, or white glove delivery services that include installation, assembly or removal of packaging and disposal of old items.
These services can be part of a premium plan that provide customers and shippers with the multiplicity of options they are looking for.
8 Track results and make data-driven adjustments

When delivery data is captured via technology solutions, management can understand how fleet and drivers perform, breaking down elements like loading & dwell time, on-time delivery rate, number of deliveries, OTD (on time delivery) success rate, and customer satisfaction.
This data helps companies gain actionable insights into their delivery KPIs and make data-driven decisions that can improve delivery efficiency, boost customer satisfaction, and lower the cost to deliver.
You also can harness analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) solutions such as machine learning to drill down into your data for specialized improvements. For example, you might find that certain delivery problems occur mainly within a delivery specific zip code, or when using a specific fleet. We also see this in the white glove space for carriers who like to better understand what the time on-site is for certain products.
Making adjustments accordingly can dramatically improve your on time delivery rates and customer satisfaction.
How to improve delivery efficiency
Implementing these best practices depends heavily on your selection of suitable technology to handle key tasks such as route optimization and scheduled delivery pending message notifications. An ideal platform should include features such as:
- Last-mile experience optimization tools such as a centralized system for tracking inventory through its journey and automated, real time alerts to customers and dispatchers with the updated delivery status
- Third party delivery integration for connecting with shipping companies seamlessly
- Fleet and driver management tools for handling tasks such as viewing available drivers and issuing driver payments
- Dispatching and routing automation tools
- A driver app to help drivers load items faster into trucks, get through their tasks faster, and deliver more
- Integrations that connect your delivery system and resources – internal and external – with your supply chain
Not all platforms will include all these features. Do your due diligence to select the platform appropriate for your needs.
Optimize your planned delivery procedures to maximize customer satisfaction
Offering scheduling delivery as part of an omnichannel fulfillment strategy is critical to meeting customer expectations today. But growing customer demand for fast delivery, inefficiencies of scheduling by phone, the need for precise planning, the risk of plans getting disrupted by exception events and the necessity of real-time communication.
Best practices for addressing these issues revolve around accurate, optimized route planning, supported by real-time communication such as scheduled delivery pending message notifications to make adjustments to changes.
These best practices are best implemented using delivery technology to optimize route planning and shipment management. Coupled with analytics, this can enable you to continuously improve your performance through small, ongoing adjustments.
Making these types of adjustments can help you improve your delivery service and lower your delivery cost.
Have multiple delivery models in your arsenal
As businesses prioritize supply chain optimization and adopt new tools and strategies – including customer-centric operations and automated delivery solutions that connect resources – they can become more efficient and cost-effective, while providing customers with the convenience they’re looking for from their delivery.
To optimize scheduled delivery, it’s imperative to choose the right last mile delivery platform. An ideal platform may include a wide range of features such as last-mile inventory tracking, order fulfillment, fleet management, automated dispatching and routing and third-party delivery and software integration. Some delivery apps may have one or more of these features, while best-in-class tools will have a full range of features. Choose the solution which best meets your needs.